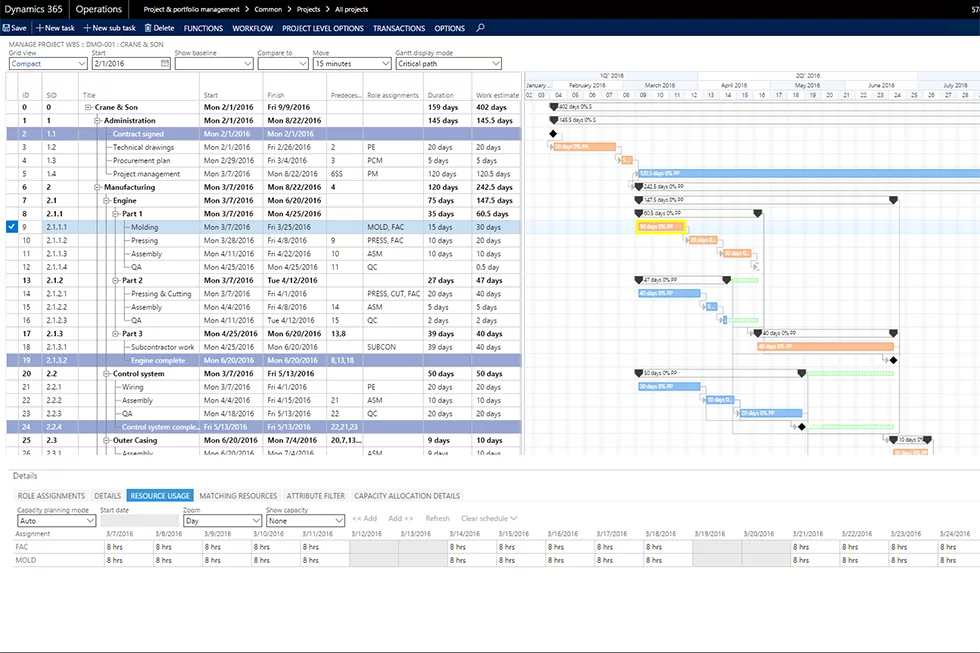
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical outline of the tasks required to complete a project. The WBS “breaks down” the structure of a project into manageable deliverables. Each deliverable is assigned a task, or series of tasks that can be further broken down into subtasks to meet the needs of the project.
The advantage of using a WBS as part of project lifecycle management is that is takes large, complex projects and breaks them into smaller, more manageable tasks that can be assigned to specific people or teams to deliver.
Purpose of the Work Breakdown Structure
The primary purpose of the WBS is too plan the schedule for the project. Each task duration is planned in conjunction with its required predecessors and following tasks. The WBS then provides an overall plan so that the project manager can see how the project should progress and manage the workflow appropriately.
Related: What is a Cost Breakdown Structure?
WBS Components
The parts of the WBS include:
- Tasks – a number, ID, title, and description of each task.
- Task Owner – who is responsible for completing the task.
- Task Dependency and Predecessors – linking two tasks together if one depends on the completion of the other.
- Start and Finish Date of Task – estimates the time each task will take and ultimately the entire project.
- Duration – how long will each task take on the calendar (usually number of days or hours).
- Work Estimate – how many hours/days of work are required to complete the task (combining all resource hours together if working in parallel).
- Task Status – whether each task is assigned to an owner/resource, started, in progress, late, complete, etc.
- Gantt Chart – a visualization of the WBS with tasks represented graphically over time.
Work Breakdown Structure Example
The WBS is a central component of many project management tools, some PPM solutions offer a limited WBS as well. However a full operational WBS example is part of Project Business Automation, as it acts as the primary schedule against which all other activities and system operations are executed.
See How the Work Breakdown Structure in PBA Works
Eliminate standalone project management applications and the overhead needed to manage them.
- Leverage the project schedule to accurately build a labor budget, time-phase earned value estimates, and generate cash flow projections
- Apply the timeline directly to MRP for production orders, and automatically constrain the schedule based on procurement or production delays
- Staff projects more efficiently and automatically feed status updates, issues and work estimates back to the schedule from the timesheet
- Evaluate cost to complete with real-time work estimates from the schedule
- Report on the financial impact of schedule changes immediately
To learn how a WBS should be integrated into the rest of your project processes and systems, Download the Project Business Automation Blueprint. It is the definitive guide to creating a comprehensive business system for your Project Business that ties together your project operations and financials seamlessly.
The Difference Between WBS and CBS
The WBS is an operational plan – what work will be done, how it will be completed and on what schedule. The Cost Breakdown Structure (CBS) is the financial plan of the project. Many companies use the WBS as their financial plan as well. However, this approach often leads to financial problems with the project. The WBS is far to granular to be able to manage costs effectively. Or, it can be far to general to get the right cost details and apply them to the appropriate general ledger areas.
The CBS is the answer. The CBS is linked to the WBS, but allows for a complete breakdown of the project for financial purposes, which enables effective project cost control and earned value analysis.